Lupus erythematosus (LE) is an insidious autoimmune disease that has many faces. It can manifest itself through a variety of symptoms and affect different organs and systems in the body. The disease is chronic and can go through periods of mild symptoms and acute flare-ups.
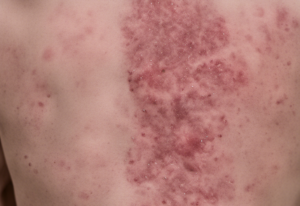
This guide will give you a quick overview of lupus erythematosus, from its causes and symptoms to treatment options and preventive measures.
What is lupus erythematosus?
Lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells and tissues. This leads to inflammation and damage to various organs and systems of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and nervous system.
There are several forms of lupus erythematosus, with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) being the most well-known and severe.
Causes and risk factors
The exact causes of lupus erythematosus are not fully understood. However, it is believed that a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors may contribute to the development of the disease. Some risk factors include:
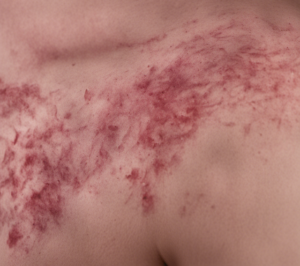
- Genetic predisposition: There are certain genes that can increase the risk of lupus erythematosus.
- Hormonal factors: Hormones, especially estrogens, appear to play a role in the development of lupus.
- Environmental factors: Infections, stress, sunlight, and certain medications can trigger lupus flare-ups.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Lupus erythematosus can cause a wide range of symptoms that often resemble other diseases. The most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Joint pain and swelling
- Rashes, especially the butterfly-shaped rash on the face
- Fever with no known cause
Due to the butterfly-shaped rash, LE is also called butterfly lichen or butterfly disease .
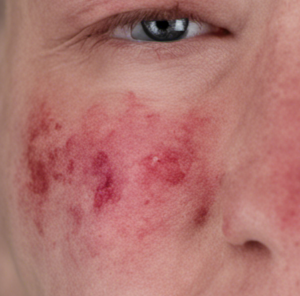
Diagnosing lupus erythematosus can be challenging and is based on a combination of clinical examination, symptoms, and laboratory tests.
Treatments
Treatment for lupus erythematosus aims to relieve symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and improve quality of life. These include:
- Drug therapy: including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarials, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants.
- Healthy lifestyle habits: eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Prevention and lifestyle with lupus erythematosus
Proactive management of lupus erythematosus can help prevent flare-ups and slow disease progression. These include:
- Regular medical check-ups
- Sun protection: Because sunlight can trigger lupus flare-ups, it’s important to protect the skin and use sunscreen.
- Maintain healthy lifestyle habits: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction can go a long way in improving quality of life.
Lupus erythematosus is a complex and challenging disease that, in addition to its primary symptoms, can also lead to consequential damage, such as scarring. However, with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, sufferers can live an active and fulfilling life.
We hope this guide will serve as a first step towards a better understanding of this disease in order to be able to take the necessary measures to improve the quality of life.