When the leaves fall and the days get shorter, not only the time of colorful scarves and warming teas begins, but also the high season for colds and flu. As we prepare to fight viruses and bacteria, one crucial factor is often overlooked: the health of our gut. This article is dedicated to the central role that a healthy gut plays in cold season and provides practical tips on how to boost your gut health.
Our gut is more than just a digestive organ; it is the center of our immune system. A healthy intestinal flora, consisting of trillions of microorganisms, is crucial for the defense against pathogens. This microflora supports not only digestion, but also the production of antibodies and other immune cells. A disturbed intestinal flora can lead to a weakened immune response, which makes us more susceptible to infections.
Structure and function of the human intestine
The human gut is a central organ of our body that plays a crucial role in health and the immune system. It consists of two main parts: the small intestine and the large intestine.
The small intestine
Center of Nutrient Uptake
The small intestine is responsible for digesting and absorbing nutrients from our food. It is divided into three areas and has a special structure with many small protrusions that allow efficient absorption of nutrients.
The large intestine
Home of gut bacteria
The large intestine is mainly responsible for water absorption and processing of undigested food residues. It is home to a diverse community of bacteria, the so-called gut microbiome. These bacteria are important for the digestion of certain food components and the production of some vitamins.
Immune system in the intestine
Similar to the lungs, the intestine is one of the main contacts between the inside of the body and the external environment. Numerous substances, including potential pathogens, enter the intestines through food intake. Therefore, it is of great importance that the immune system is strongly represented here in order to be able to react effectively to possible threats. A large part of our immune system is therefore located in the intestine.
Gut bacteria and immune cells in the gut help fight off pathogens and promote a healthy immune response. In the cold season, a well-functioning intestine is therefore particularly important to reduce the risk of infections.
Bacteria as allies
The gut microbiome, a community of trillions of bacteria in the colon, is important for the immune system. These bacteria…
- Protect against pathogens: They compete with harmful microorganisms for nutrients and habitat, preventing pathogens from entering and multiplying.
- Train the immune system: The presence of these bacteria trains the immune system to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances. This helps to avoid overreactions such as allergies.
Nutrients and Immune Function
Nutrient absorption in the small intestine is important for the functioning of the immune system. Certain nutrients, such as vitamins and trace elements, are essential for the formation and activity of immune cells. A deficiency of these nutrients can weaken the immune system as a whole.
Immune cells in the intestine
A large part of the body’s immune cells are located in the intestine to defend against pathogens. These include:
- Lymphocytes: Specialized white blood cells that produce antibodies and attack foreign pathogens.
- GALT (Gut-associated lymphoid tissue): A network of lymphoid tissue in the gut that plays a central role in the immune response. Here, immune cells mature and are trained for possible threats.
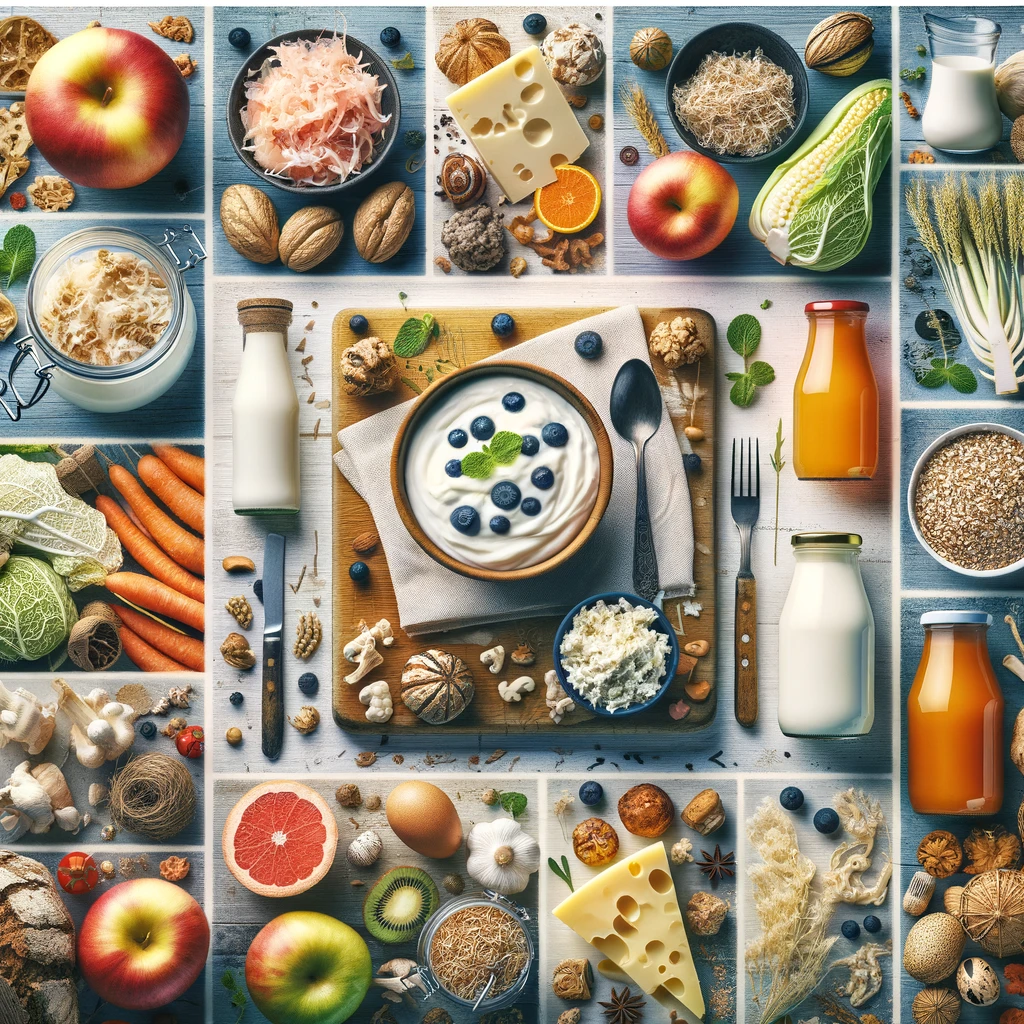

Nutrition and Gut Health
A balanced diet is the be-all and end-all for a healthy intestinal flora. Foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, provide good bacteria to the gut. Prebiotics, which are found in whole grains, legumes, garlic, onions, and some vegetables, serve as food for these good bacteria. A high-fiber diet promotes the diversity of the intestinal flora and supports digestion, which in turn strengthens the immune system.
Lifestyle Factors and Gut Health
In addition to diet, other factors also affect the health of our gut. Chronic stress, lack of sleep and lack of exercise can have a negative impact on the intestinal flora. Stress, for example, can increase the permeability of the intestines, which can lead to inflammation and a weakened immune system. Sufficient sleep and regular exercise are therefore not only good for the mind and body, but also for the intestines.
Practical tips to strengthen gut health during the cold season
To boost your gut health during cold season, keep the following tips in mind:
- Incorporate fermented foods into your diet on a daily basis.
- Make sure you get a balanced intake of fiber from whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and highly processed foods, as these can negatively affect the intestinal flora.
- Exercise regularly to support bowel movement and flora.
- Make sure you get enough sleep to regenerate the body and thus also the intestines.
Summary
The health of our gut plays a crucial role in our immune system and, therefore, our ability to fight infections during cold season. A balanced diet, a healthy lifestyle and taking into account the special needs of our intestines can go a long way in strengthening our defenses.
We hope this article provides you with helpful insights and practical tips on how to strengthen your gut health. Stay healthy and take care of your gut!
